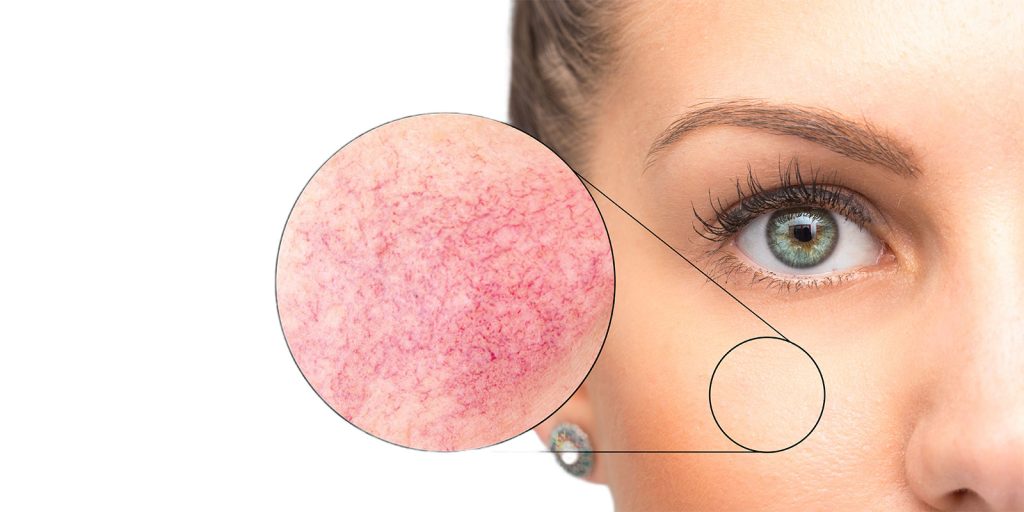
Pigmenttiläiskien hoito
Ihon pigmenttimuutokset ovat:
synnynnäiset ihon pigmenttisoluhäiriöt, kuten lentigot ja cafe au lait
-läiskätpisamat ja maksaläiskät
auringon aiheuttamat värimuutokset
Liikapigmettia esiintyy eritysesti auringovalo-alueilla: kasvoissa, kaulalla ja dekoltee-alueella sekä kädenselissä.
Yleinen ongelma naisilla ovat maksaläiskät, johon vaikuttavat perimä, aurinko ja hormonit. Myös mekaaninen ärsytys voi aiheuttaa ihon tummumista. Naisilla esiintyy kaulan sivulla ruskeapunaista ihon tummumista (Civatten poikiloderma), johon vaikuttavat kosmeettiikkatuotteet ja aurinko. Ihon tummuminen voi johtua myös laserhionnasta.
Maksaläiskät (Melasma) ovat pääasiallisesti vain naisilla esiintyviä ihon pigmentin muutoksia. Maksaläiskät ilmestyvät naisilla yleensä kasvoihin tummina läikkinä ja useimmiten kesäkuukausina auringonvalon määrän ollessa huipussaan.Yleisimmät paikat ovat otsa, poskipäät, ylähuuli, nenä sekä leuka.
Tärkeimmät riskitekijät ovat auringonvalolle altistuminen ja naishormonit. Usein maksaläiskät ilmaantuvat raskauden aikana tai e-pillereiden aloittamisen jälkeen. Ihon melanosyytit tuottavat liikaa pigmenttiä aiheuttaen värimuutoksen. Maksaläiskiä voidaan hoitaa, mutta hoidon onnistumisen edellytyksenä on tarkka aurinkosuojaus aina aikaisin keväästä alkaen.
Pinnallisia pigmenttimuutoksia voidaan hoitaa värilaserilla tai ihon kuorintatoimenpiteillä.
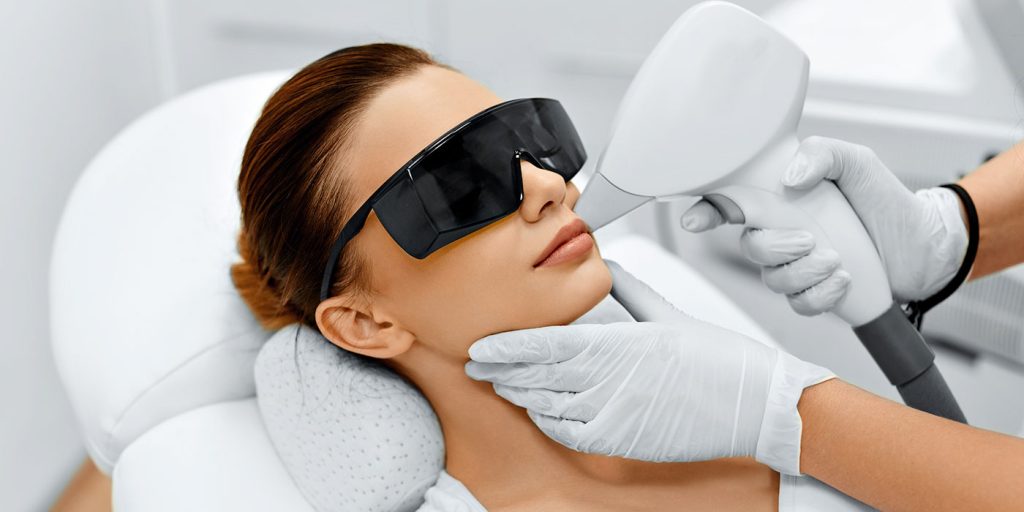
Tehokkaimmaksi pigmenttimuutosten hoitomuodoksi on laserhoito.
Hoitomenetelmä
Kahden energian eli valoimpulssin sekä radiofrekvenssin vaikutettua pigmenttiin, se lämpenee ja pigmentti hajoaa. Ihon pigmenttimuutokset alkavat tummua välittömästi hoidon jälkeen ja iho saattaa lievästi punoittaa. Hoidetulla alueella voi olla hiukan turvotusta. Nämä oireet kestävät yleensä muutamasta tunnista yhteen vuorokauteen. Punotusta voi halutessaan peittää meikillä. Tummentuneet kohdat hilseilevät ja häviävät muutaman viikon kuluttua toimenpiteestä.
Ennen hoitoa
ei voida kahden viikon aikana käyttää ihoa ruskeuttavia tuotteita eikä hoidoa anneta voimakkaasti ruskettuneelle iholle. Hoitoa ei anneta, mikäli potilaalla on sydämentahdistin tai defibrillaattori eikä myöskään raskauden tai imetyksen aikana.
Hoidon jälkeen
On tärkeää suojata iho auringolta hyvin paranemisprosessin aikana ja sen jälkeen, uusien pigmenttimuutosten välttämiseksi.
Hoidon jälkeen aluetta on hyvä kuoria ja uusia, jotta hajonnut pigmentti nousisi mahdollisimman nopeasti ihon pintaan ja kuoriutuisi pois.
 ENG (Coming soon)
ENG (Coming soon)